Test Equipment Makes the Difference
The ability to independently control both temperature and pressure on a pouch cell during cycling is a unique capability in both research and the commercial market. Our equipment enables the direct measurement of phenomena—and their dependencies on temperature and pressure—that, until now, have only been theorized in scientific literature.
Investigation of the piezoelectrochemical transducer effect with respect to temperature
Applying mechanical pressure to a Li-ion battery induces a variation in its open-circuit voltage, resembling the behavior observed in piezoelectric materials. However, the magnitude of this effect—as well as its dependency on pressure levels and temperature—remains insufficiently quantified in the current literature.

Data driven Digital Twin calibrated on thermo-electro-mechanical measurements based on an extended HPPC test protocol
Building a reliable digital twin of a battery is challenging when coupled models—thermal, electrical, and mechanical—are calibrated using data from separate test setups. Our system enables a unified sensitivity study based on a single HPPC test protocol, allowing comprehensive modeling of the cell’s thermo-electro-mechanical behavior.

Analysis of the breathing phenomenon with respect to temperature and pressure
The breathing phenomenon refers to the reversible expansion of a Li-ion cell caused by the intercalation and de-intercalation of lithium ions within the anode structure. To accurately quantify the extent of this expansion—and understand its dependency on temperature and average pressure levels—a dedicated phenomenological study is required.

Sensitivity study of electrical performaces with respect to pressure and temperature
The electrical performance of a pouch-format Li-ion battery was investigated under varying temperature and pressure conditions. The findings of this study have been successfully published in a peer-reviewed journal.

Analysis of the swelling phenomenon with respect to temperature and pressure
The irreversible expansion of Li-ion cells during their life, known as swelling, must be investigated with respect to the working temperature and the average applied pressure.

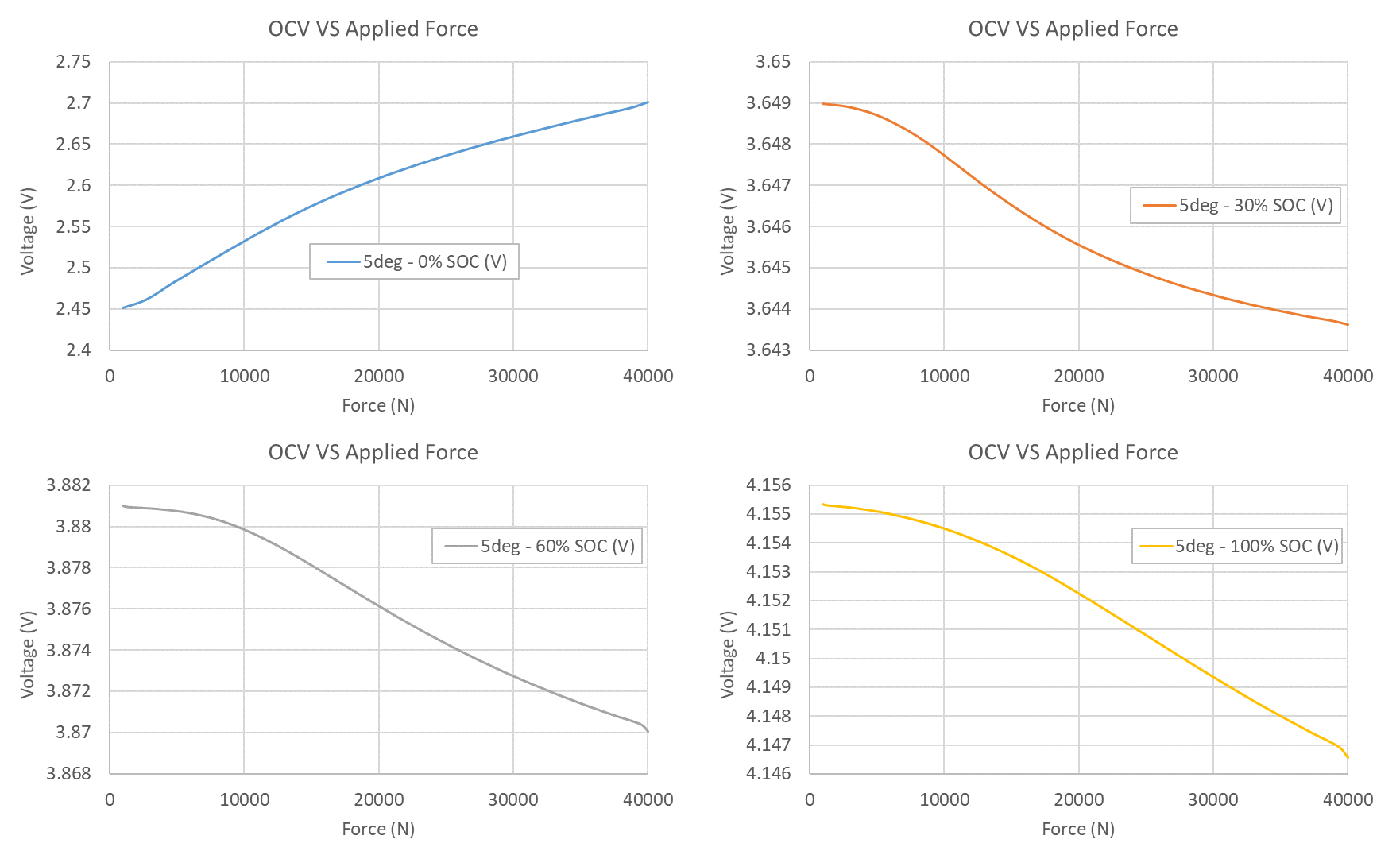
Influence of pressure and temperature on the open circuit voltage curve
The open-circuit voltage (OCV) curve of a Li-ion cell is known to vary with temperature—a well-documented phenomenon in the literature. However, the influence of mechanical pressure on the amplitude of this voltage variation remains largely unexplored and has yet to be systematically investigated.
